What Edible Plants Benefit from Coffee Grounds? This question, often posed by eco-conscious gardeners, delves into the surprising world of coffee grounds as a valuable resource for enriching soil and promoting plant growth. Beyond their aromatic beverage potential, coffee grounds possess a unique blend of nutrients and properties that can significantly enhance the health and productivity of various edible plants.
Coffee grounds are rich in nitrogen, a crucial element for healthy plant growth, along with other essential nutrients like phosphorus and potassium. They also improve soil structure, promoting aeration and water retention. The organic matter in coffee grounds stimulates microbial activity, leading to a more fertile and thriving soil ecosystem.
Benefits of Coffee Grounds for Plants: What Edible Plants Benefit From Coffee Grounds?
Coffee grounds, the leftover residue after brewing coffee, are a valuable resource for gardeners and plant enthusiasts. They offer a plethora of benefits, enriching the soil and promoting healthy plant growth.
Nutritional Composition of Coffee Grounds
Coffee grounds are rich in essential nutrients that plants need to thrive. These nutrients include:
- Nitrogen (N):A key element for promoting healthy leaf growth and chlorophyll production.
- Phosphorus (P):Vital for root development, flowering, and seed production.
- Potassium (K):Essential for strong stems, disease resistance, and overall plant vigor.
- Magnesium (Mg):A component of chlorophyll, crucial for photosynthesis and energy production.
- Calcium (Ca):Contributes to cell wall structure and helps regulate nutrient uptake.
In addition to these macronutrients, coffee grounds also contain micronutrients like iron, manganese, and zinc, which play essential roles in various plant functions.
Impact of Coffee Grounds on Soil Health
Coffee grounds have a positive impact on soil health, improving its physical and biological properties.
- Improved Aeration:Coffee grounds, with their porous structure, enhance soil aeration, allowing for better oxygen circulation to plant roots. This is particularly beneficial for compacted soils.
- Water Retention:Coffee grounds act as a natural sponge, absorbing and retaining moisture. This helps prevent soil from drying out too quickly, ensuring adequate water availability for plants.
- Enhanced Microbial Activity:Coffee grounds provide a rich source of organic matter, which stimulates microbial activity in the soil. These beneficial microbes break down organic matter, releasing nutrients that plants can access.
Coffee Grounds as a Natural Fertilizer
Coffee grounds can serve as a natural fertilizer, enriching the soil with essential nutrients.
- Nitrogen Enrichment:Coffee grounds contain a significant amount of nitrogen, which is readily available to plants. This nitrogen promotes lush foliage and vibrant green color.
- Phosphorus Enhancement:While coffee grounds have lower phosphorus content than other fertilizers, they still contribute to phosphorus availability in the soil. This is crucial for root development and overall plant vigor.
- Potassium Supplementation:Coffee grounds contain a moderate amount of potassium, which plays a vital role in plant health, particularly in disease resistance and stem strength.
Edible Plants That Thrive with Coffee Grounds
Coffee grounds are a valuable resource for gardeners, offering a wealth of benefits for various plants. Their rich nutrient content and acidic nature make them particularly beneficial for certain edible plants, enhancing their growth, yield, and overall health.
Acid-Loving Edible Plants
Coffee grounds are known to lower soil pH, making them ideal for acid-loving plants. These plants thrive in slightly acidic soil conditions, typically with a pH between 5.5 and 6.5.
- Blueberries:Coffee grounds can help create the acidic soil environment blueberries need to thrive, promoting vigorous growth and abundant fruit production. Studies have shown that using coffee grounds as a soil amendment can increase blueberry yields by up to 20%.
- Cranberries:Similar to blueberries, cranberries benefit from the acidic environment provided by coffee grounds. This helps them produce larger, healthier berries with improved flavor.
- Rhododendrons:These flowering shrubs, known for their vibrant blooms, prefer acidic soil conditions. Coffee grounds can improve their growth and flowering, creating a more vibrant display.
- Azaleas:These colorful flowering shrubs, closely related to rhododendrons, also benefit from the acidic environment provided by coffee grounds. They will produce more abundant and vibrant blooms with the addition of coffee grounds to their soil.
Vegetables That Benefit from Coffee Grounds, What Edible Plants Benefit from Coffee Grounds?
Coffee grounds can also enhance the growth of certain vegetables, providing essential nutrients and improving soil structure.
- Tomatoes:Coffee grounds can help increase tomato yield and improve fruit quality. The nitrogen and other nutrients in coffee grounds promote healthy foliage and robust fruit production. They also help improve soil drainage, which is crucial for tomatoes.
- Peppers:Similar to tomatoes, peppers benefit from the added nutrients and improved drainage provided by coffee grounds. They produce larger, more flavorful peppers when grown in soil amended with coffee grounds.
- Potatoes:Coffee grounds can help increase potato yields and improve tuber quality. They provide essential nutrients and improve soil structure, creating a favorable environment for potato growth.
- Broccoli:Coffee grounds can enhance the growth and yield of broccoli. They provide essential nutrients and improve soil structure, promoting healthy foliage and larger, more flavorful florets.
Herbs That Thrive with Coffee Grounds
Many herbs, particularly those that prefer slightly acidic soil conditions, benefit from the addition of coffee grounds.
- Rosemary:Coffee grounds can help rosemary grow larger and more robust, producing a more abundant supply of fragrant leaves. They also improve soil drainage, which is crucial for rosemary.
- Basil:Coffee grounds can enhance the growth and flavor of basil. They provide essential nutrients and improve soil structure, promoting healthy foliage and flavorful leaves.
- Mint:Coffee grounds can help mint grow more vigorously and produce a more abundant supply of leaves. They also improve soil drainage, which is crucial for mint.
- Oregano:Coffee grounds can enhance the growth and flavor of oregano. They provide essential nutrients and improve soil structure, promoting healthy foliage and flavorful leaves.
Comparing the Effects of Coffee Grounds on Edible Plants
Plant |
Growth Rate |
Yield |
Overall Health |
|---|---|---|---|
Blueberries |
Increased |
Increased by up to 20% |
Improved |
Cranberries |
Increased |
Increased |
Improved |
Tomatoes |
Increased |
Increased |
Improved |
Peppers |
Increased |
Increased |
Improved |
Potatoes |
Increased |
Increased |
Improved |
Broccoli |
Increased |
Increased |
Improved |
Rosemary |
Increased |
Increased |
Improved |
Basil |
Increased |
Increased |
Improved |
Mint |
Increased |
Increased |
Improved |
Oregano |
Increased |
Increased |
Improved |
Practical Applications of Coffee Grounds in Gardening
Coffee grounds, a readily available byproduct of our daily caffeine fix, offer a wealth of benefits for gardeners. They act as a natural soil amendment, improving soil structure, aeration, and drainage while enriching it with essential nutrients.
Incorporating Coffee Grounds into Soil
There are several methods to introduce coffee grounds into your garden, each with its own advantages.
Direct Application
Directly applying coffee grounds to the soil is a simple and effective method. However, moderation is key. Excessive application can lead to an acidic environment, potentially detrimental to some plants. For most plants, a thin layer of coffee grounds spread around the base of the plant, about 1/4 inch thick, is sufficient.
Avoid piling grounds directly against the stem, as this can hinder airflow and promote fungal growth.
Composting
Adding coffee grounds to your compost pile is a great way to enhance its nutrient content and accelerate decomposition. Coffee grounds are rich in nitrogen, which is crucial for plant growth. They also provide carbon, balancing the nitrogen-to-carbon ratio in your compost.
Aim for a 1:1 ratio of coffee grounds to other organic materials in your compost pile.
Worm Castings
Worm castings, the excrement of composting worms, are a highly concentrated and beneficial fertilizer. Worms readily consume coffee grounds, breaking them down into readily available nutrients. This method is particularly beneficial for plants that require a constant supply of nutrients, such as vegetables and flowering plants.
Optimal Ratios and Frequency of Application
The optimal ratio and frequency of applying coffee grounds vary depending on the plant type and soil conditions.
Acid-Loving Plants
Acid-loving plants, such as blueberries, rhododendrons, and azaleas, thrive in acidic soil. Coffee grounds, being naturally acidic, can be applied more frequently to these plants. A layer of 1/2 inch of coffee grounds around the base of the plant, applied every 2-3 weeks, is generally suitable.
While coffee grounds can enrich the soil for edible plants like blueberries and azaleas, they can also add a touch of natural beauty to your home. If you’re looking for ways to enhance your indoor greenery, consider incorporating some stunning hanging plants, like the cascading foliage of a spider plant or the vibrant blooms of a fuchsia, into your living space.
Stunning Hanging Plants to Transform Your Living Room offers a variety of inspiring ideas. And, when it comes to your edible plants, remember that coffee grounds can help improve drainage and deter pests, ensuring a healthy and thriving garden.
Neutral-Loving Plants
Plants that prefer neutral soil, such as roses, tomatoes, and peppers, can tolerate moderate amounts of coffee grounds. However, excessive application can lead to an acidic environment, hindering their growth. A thin layer of coffee grounds, about 1/4 inch thick, applied every 4-6 weeks, is generally recommended.
Alkaline-Loving Plants
Alkaline-loving plants, such as lavender, rosemary, and thyme, are sensitive to acidic conditions. Coffee grounds should be used sparingly with these plants. A thin layer, about 1/8 inch thick, applied every 6-8 weeks, is sufficient.
Preparing a Coffee Grounds-Based Fertilizer
Here’s a step-by-step guide to preparing a coffee grounds-based fertilizer:
1. Gather your ingredients
While coffee grounds can be a great amendment for a variety of plants, including blueberries and rhododendrons, they can also be used to create a lush vertical garden. If you’re limited on space, consider hanging planters, and for inspiration on how to arrange them effectively, check out this guide on How to Arrange Multiple Hanging Plants in a Small Space.
Once you’ve got your vertical garden set up, you can experiment with other coffee ground-loving plants, like azaleas and ferns.
You’ll need coffee grounds, water, and a container.
2. Mix the ingredients
Combine coffee grounds and water in a ratio of 1:1 by volume.
3. Let it ferment
Cover the container and let the mixture ferment for 2-3 weeks, stirring occasionally.
4. Dilute before use
Dilute the fermented mixture with water in a ratio of 1:10 before applying to plants.
Note:This fertilizer is best applied to the soil around the base of the plant, avoiding direct contact with the leaves.
Considerations and Precautions
While coffee grounds offer numerous benefits for edible plants, it’s crucial to acknowledge potential drawbacks and implement strategies to mitigate them. Overusing coffee grounds can lead to soil acidity issues and attract pests, potentially impacting plant health and yield.
Soil Acidity
Coffee grounds are acidic, with a pH ranging from 4.5 to 6.5. Adding large quantities to the soil can lower its pH, potentially creating an unfavorable environment for certain plants that prefer neutral or alkaline conditions.
- Monitoring Soil pH:Regularly testing soil pH is essential to determine if coffee grounds are impacting its acidity levels. A pH meter or soil testing kit can be used to measure the pH, which should be within the optimal range for the specific plants being grown.
- Adjusting Soil pH:If the soil becomes too acidic, it can be adjusted using various methods:
- Liming:Applying agricultural lime, a natural calcium carbonate, helps raise soil pH by neutralizing acidity.
- Wood Ash:Wood ash, a byproduct of burning wood, is another natural source of calcium carbonate that can be used to increase soil pH.
- Dolomite Lime:Dolomite lime contains magnesium and calcium carbonate, providing essential nutrients while raising soil pH.
Pest Attraction
Coffee grounds can attract certain pests, particularly slugs, snails, and fungus gnats. These pests are attracted to the moist, decaying organic matter of the grounds, which can lead to damage to plants.
- Controlled Application:Applying coffee grounds in moderation and avoiding excessive accumulation around plants can minimize pest attraction.
- Pest Control:If pest infestations occur, various methods can be employed:
- Diatomaceous Earth:This natural, abrasive powder dehydrates and kills slugs, snails, and other soft-bodied insects. It can be sprinkled around plants as a barrier.
- Copper Tape:Copper tape placed around the base of plants can deter slugs and snails from climbing up.
- Neem Oil:This organic insecticide derived from the neem tree can be used as a spray to control fungus gnats and other pests.
Sustainable Gardening Practices
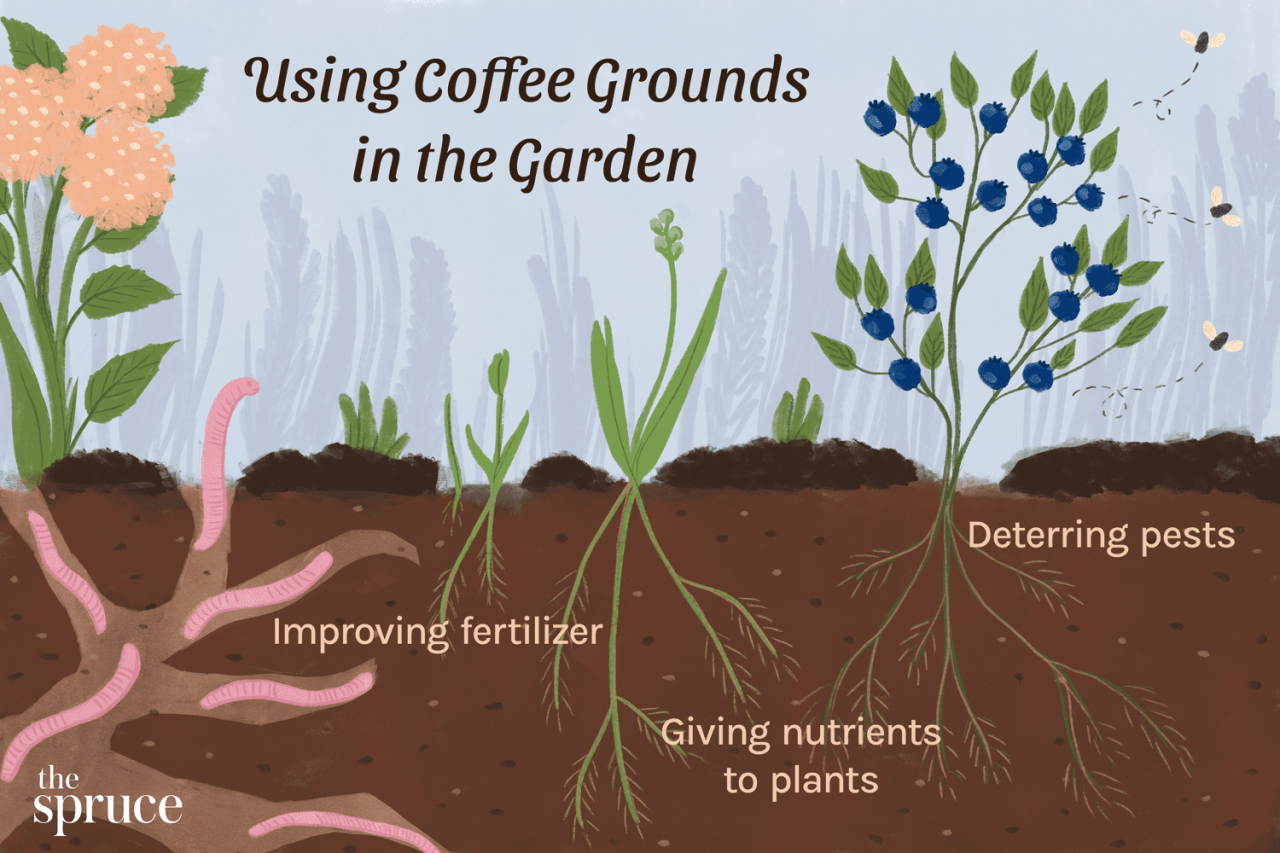
Using coffee grounds in your garden aligns with sustainable gardening principles, promoting a more eco-friendly approach to plant care. Coffee grounds are a natural, readily available resource that can benefit your plants and the environment.
Reducing Waste and Promoting Soil Health
Coffee grounds offer a sustainable alternative to synthetic fertilizers, reducing waste and promoting soil health. By diverting coffee grounds from landfills, you contribute to a more sustainable waste management system. The decomposition of coffee grounds enriches the soil with essential nutrients, improving soil structure and promoting healthy plant growth.
Creative Uses for Coffee Grounds Beyond Fertilization
Coffee grounds have multiple applications in gardening beyond fertilization. They can be used as a natural mulch, helping to retain moisture, suppress weeds, and regulate soil temperature. Coffee grounds can also be incorporated into compost piles, enhancing the decomposition process and creating a nutrient-rich soil amendment.
Coffee grounds can be used as a natural pest repellent, particularly for slugs and snails, due to their acidity.
Coffee Grounds for a More Eco-Friendly Lifestyle
Incorporating coffee grounds into your gardening practices promotes a more eco-friendly lifestyle. By reducing reliance on synthetic fertilizers and pesticides, you minimize your environmental footprint. The use of coffee grounds encourages a closed-loop system, utilizing readily available resources to enhance plant growth and soil health.
Closure

By embracing the use of coffee grounds, gardeners can create a sustainable and flourishing ecosystem for their edible plants. This natural resource, often considered waste, transforms into a valuable tool for promoting healthy growth and yields. Whether directly applied to the soil, composted, or used as a mulch, coffee grounds offer a simple and effective way to enhance the garden’s vitality, while minimizing environmental impact.
Essential Questionnaire
Can I use coffee grounds on all plants?
While coffee grounds benefit many plants, they are acidic and may not be suitable for all. Acid-loving plants like blueberries and rhododendrons will thrive, while others may require pH adjustments.
How often should I apply coffee grounds?
The frequency depends on the plant type and soil condition. A general rule is to apply a thin layer every few weeks, adjusting based on plant needs.
Can I use coffee grounds directly from the coffee maker?
Yes, but it’s best to let them cool and dry slightly before applying to prevent potential scalding of plant roots.
